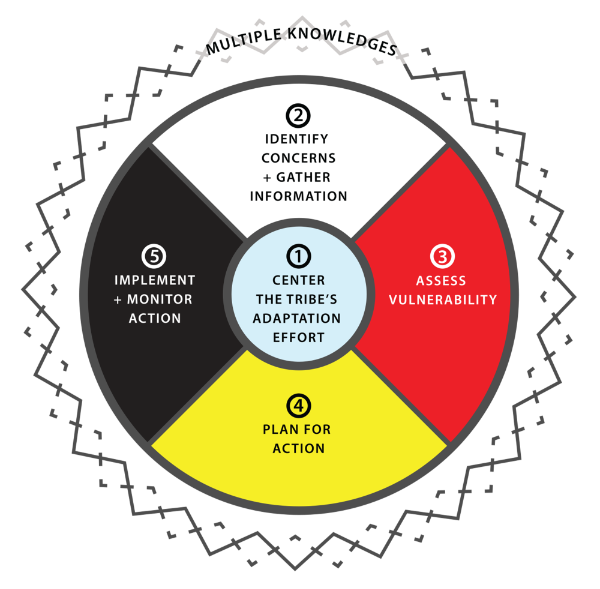
Step 2. Identify Concerns & Gather Information
Identify the Tribe’s climate-related concerns and gather information from multiple perspectives to better understand the challenges and set the stage for assessing vulnerability and planning for action.
Step 2 Content
Click the icon above (or scroll lower on the page) to directly access the main Step content.
Step 2 Checklist
Click the icon above to download an easy-to-use checklist to use while working through Step 2.
Step 2 tribal Examples
Click the icon above to see examples from Tribal climate initiatives across the US specific to Step 2.
Activity 1: Gathering and Application of Relevant Traditional Knowledges
Build on the ways in which the Tribe may already incorporate Traditional Knowledges in Tribal planning or policy activities.
“These recent efforts are a continuation of the work our elders have done for years in observing and considering climate change on our lands.”

Guiding Questions
Helpful questions to consider during this activity.

Traditional Knowledges
Considerations for integrating and protecting
Traditional Knowledges during this activity.
Activity 2: Identify and Organize Key Concerns
While all concerns are important, organizing key concerns into planning areas relevant to existing programs and departments can facilitate implementation of adaptation actions.
“This selection of Shared Concerns was not a prioritization of any issue or resource, as all species, resources, and habitats identified by the member tribes are interconnected and important. USRT [Upper Snake River Tribes Foundation] sees an urgent need to assess the climate change vulnerability for ALL Shared Concerns identified by USRT member tribes, perhaps under future funding and vulnerability assessment efforts.”

Guiding Questions
Helpful questions to consider during this activity.

Traditional Knowledges
Considerations for integrating and protecting
Traditional Knowledges during this activity.
Community Engagement Checkpoint
Working collaboratively with staff, community members, Elders, Tribal leadership, and other partners is a great way to identify the needs and concerns of the community.
Documentation Checkpoint
Document all the identified concerns noting which will be reserved for future work.
Activity 3: Document Observed Changes from Multiple Perspectives
Understanding past climate and environmental changes and how they have affected the key concerns from multiple perspectives can help ground the assessment, enhance community support, and set the stage for assessing future climate-related risks.
“Elder observations indicate that the climate has noticeably changed within their lifetime and as stated prior, the knowledge they gained from parents, grandparents, and great grandparents goes back at least three generations. These first-hand accounts of the impacts of climate change further demonstrate its effect on the Tribes”

Guiding Questions
Helpful questions to consider during this activity.

Traditional Knowledges
Considerations for integrating and protecting
Traditional Knowledges during this activity.
Community Engagement Checkpoint
Gathering information from the Tribal community on observed changes can help create a holistic understanding of how the Tribe is experiencing climate change.
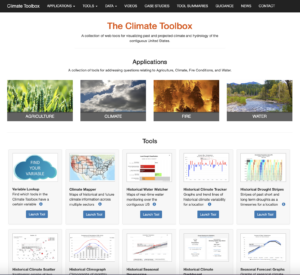
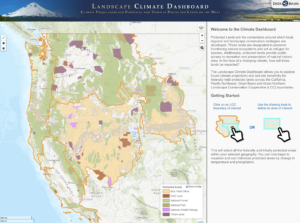
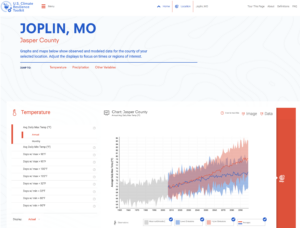
Activity 4: Collect Regional and Local Climate Change Projections
Understanding how climate is expected to change in the future informs the vulnerability and risk assessment of key concerns.
“The changes already being seen are substantial, and by the end of the century we will likely be facing unprecedented changes to our natural environment and the economies that depend on it.”

Guiding Questions
Helpful questions to consider during this activity.

Traditional Knowledges
Considerations for integrating and protecting
Traditional Knowledges during this activity.
Documentation Checkpoint
Synthesize all of the relevant collected information, ensure that it is consistent with the goals of the planning process, and include it in the adaptation plan.